First Case of Mopox Virus from West African Clade Detected in India
Health authorities in India have confirmed the presence of the Mopox virus in an isolated patient, marking the first known case of the virus belonging to the West African Clade Two in the country. The discovery has raised concerns among public health officials as they work to determine the extent of the potential spread and implement necessary containment measures.
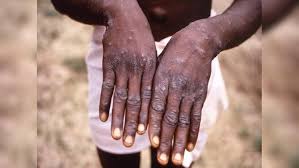
The Mopox virus, primarily found in West Africa, is similar to the monkeypox virus and poses significant health risks due to its contagious nature. The virus can lead to symptoms such as fever, rashes, and swollen lymph nodes, with severe cases potentially causing complications, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
Health officials have stated that the patient has been placed in isolation and is receiving appropriate medical care. Authorities are also conducting contact tracing and testing those who may have come into contact with the patient to prevent further transmission of the virus.
India's health ministry is closely monitoring the situation and has assured the public that preventive measures are being taken to avoid any outbreak. Medical experts are urging vigilance and strict adherence to safety protocols, including personal hygiene and avoiding contact with individuals showing symptoms.
The detection of the Mopox virus from the West African Clade Two adds to the growing list of global health concerns, and Indian health authorities are preparing to mitigate any potential risks associated with the virus's presence in the country.